OpenStack: use ephemeral and persistent root storage for different hypervisors

Computes with Ceph image backend and computes with local image backend. At some point, you might want to build hypervisor and use their local storage for virtual machine root disks. Using local storage will help you maximasing your IOs and will reduce IO latentcies to the minimum (compare to network block storage). However you will lose handy features like the live-migration (block migration is still an option but slower). Data on the hypervisors will not have a good availability level too. If the compute node crashes the user will not be able to access his virtual machines for a certain amount of time. On another hand, you want to build hypervisors that where virtual machine root disks will live into Ceph. Then you will be able to seemlessly move virtual machine with the live-migration. Virtual machine disks will be highly available so if a compute node crashes you can quickly evacuate the virtual machine disk to another compute node. Ultimately, your goal is to dissociate them, fortunately for you OpenStack provides a mechanism based on host agregate that will help you achieve your objective. Thanks agregate filters you will be able to expose these hypervisors.
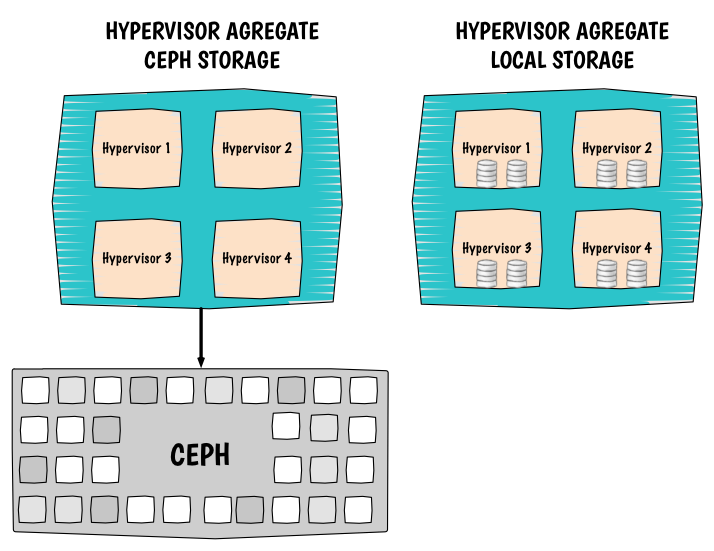
I. Compute nodes configuration
I.1. Scheduler
In order to instruct Nova that the scheduler has to run through new filters, you must add a new one called AggregateInstanceExtraSpecsFilter to the filters.
With the help of this filter the nova-scheduler will read virtual machine extra specs:
scheduler_default_filters=RetryFilter,AvailabilityZoneFilter,RamFilter,ComputeFilter,ImagePropertiesFilter,ServerGroupAntiAffinityFilter,ServerGroupAffinityFilter,AggregateInstanceExtraSpecsFilter
I.2. Local storage configuration
This is the default behavior of Nova so nothing needs to be configured, it is all default.
I.3. Ceph storage configuration
Edit your nova.conf and modify:
[libvirt]
inject_partition=-2
disk_cachemodes=network=writeback
rbd_secret_uuid=a705a325-6cfb-466c-887e-2158f9cecc29
live_migration_flag=VIR_MIGRATE_UNDEFINE_SOURCE,VIR_MIGRATE_PEER2PEER,VIR_MIGRATE_LIVE,VIR_MIGRATE_PERSIST_DEST
inject_key=False
images_rbd_pool=vms
images_type=rbd
images_rbd_ceph_conf=/etc/ceph/ceph.conf
rbd_user=cinder
For more details please visit the official Ceph documentation.
II. OpenStack configuration
Then create the aggregate that will contain the ceph compute nodes and the local storage compute nodes instances:
$ nova aggregate-create ephemeral-compute-storage |
You can use nova hypervisor-list to retrieve hypervisor names like so:
$ nova hypervisor-list |
In this exemple I will use the following mapping:
- Local storage:
- compute01
- compute02
- Ceph storage:
- compute03
- compute04
Add host to your aggregate:
$ nova aggregate-add-host ephemeral-compute-storage compute01 |
Create a new metadata for this aggregate:
$ nova aggregate-set-metadata <ephemeral-compute-storage aggregate ID> ephemeralcomputestorage=true |
Be careful if you modify the name of an aggregate all the metadata will be deleted (behavior seen on Icehouse).
Create a new flavor for the local storage and ceph storage instances:
$ nova flavor-create m1.ephemeral-compute-storage 6 4096 40 2 |
Prior to Juno
Assign to this flavor a special property:
$ nova flavor-key m1.ephemeral-compute-storage set ephemeralcomputestorage=true |
For Juno and later
$ nova flavor-key m1.ceph-compute-storage set aggregate_instance_extra_specs:cephcomputestorage=true |
Easy :)
Comments